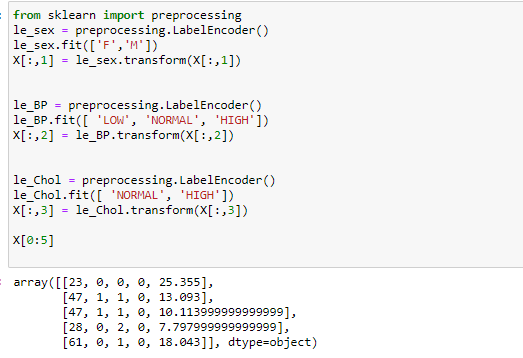
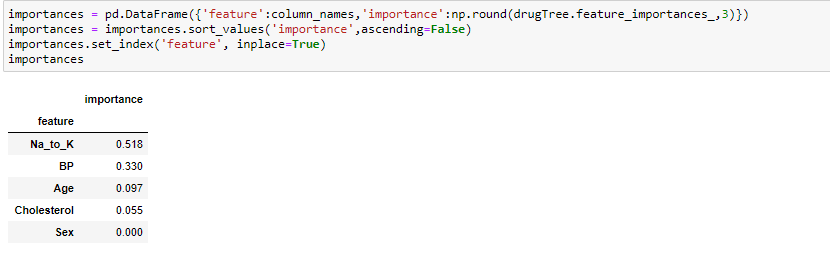
#Method 1
Code:
import re
print('Enter the text:')
text = input()
months='(Jan(?:uary)?|Feb(?:ruary)?|Mar(?:ch)?|Apr(?:il)?|May|Jun(?:e)?|Jul(?:y)?|Aug(?:ust)?|Sep(?:tember)?|Oct(?:ober)?|(Nov|Dec)(?:ember)?)'
re1=r'\w?((mor|eve)(?:ning)|after(?:noon)?|(mid)?night|today|tomorrow|(yester|every)(?:day))'
re2=r'\d?\w*(ago|after|before|now)'
re3=r'((\d{1,2}(st|nd|rd|th)\s?)?(%s\s?)(\d{1,2})?)' % months
re4=r'\d{1,2}\s?[a|p]m'
re5=r'(\d{1,2}(:\d{2})?\s?((hour|minute|second|hr|min|sec)(?:s)?))'
re6=r'(\d{1,2}/\d{1,2}/\d{4})|(\d{4}/\d{1,2}/\d{1,2})'
re7=r'(([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9])'
re8=r'\d{4}'
relist= [re1, re2, re3, re4, re5, re6, re7, re8]
print("\n\nTemporal expressions are listed below:\n")
for exp in relist:
match = re.findall(exp,text)
for x in match:
print(x)
Output:
Enter the text:
I get up in the morning at 6 am. I have been playing cricket since 2004. My birth date is 1997/9/8. It has been 2 hours since I am studying. The time right now is 12:45. He is coming today. I study till midnight everyday. It takes 2 mins to solve this problem. He is coming in January. He went abroad on 2nd March, 1999. He was working here 5 years ago.
Temporal expressions are listed below:
('morning', 'mor', '', '')
('today', '', '', '')
('midnight', '', 'mid', '')
('everyday', '', '', 'every')
now
ago
('January', '', '', 'January', 'January', '', '')
('2nd March', '2nd ', 'nd', 'March', 'March', '', '')
6 am
('2 hours', '', 'hours', 'hour')
('2 mins', '', 'mins', 'min')
('', '1997/9/8')
('12:45', '12')
2004
1997
1999
#Method 2
Code:
import re
print('Enter the text:')
text = input()
text=list(text.split("."))
months='(Jan(?:uary)?|Feb(?:ruary)?|Mar(?:ch)?|Apr(?:il)?|May|Jun(?:e)?|Jul(?:y)?|Aug(?:ust)?|Sep(?:tember)?|Oct(?:ober)?|(Nov|Dec)(?:ember)?)'
re1=r'\w?((mor|eve)(?:ning)|after(?:noon)?|(mid)?night|today|tomorrow|(yester|every)(?:day))'
re2=r'\d?\w*(ago|after|before|now)'
re3=r'((\d{1,2}(st|nd|rd|th)\s?)?(%s\s?)(\d{1,2})?)' % months
re4=r'\d{1,2}\s?[a|p]m'
re5=r'(\d{1,2}(:\d{2})?\s?((hour|minute|second|hr|min|sec)(?:s)?))'
re6=r'(\d{1,2}/\d{1,2}/\d{4})|(\d{4}/\d{1,2}/\d{1,2})'
re7=r'(([0-1]?[0-9]|2[0-3]):[0-5][0-9])'
re8=r'\d{4}'
relist= [re1, re2, re3, re4, re5, re6, re7, re8]
re_compiled = re.compile("(%s|%s|%s|%s|%s|%s|%s|%s)" % (re1, re2, re3, re4, re5, re6, re7, re8))
print("\n\n Output(with temporal expression enclosed within square bracket:\n")
for s in text:
print (re.sub(re_compiled, r'[\1]', s))
Output:
Enter the text:
I get up in the morning at 6 am. I have been playing cricket since 2004. My birth date is 1997/9/8. It has been 2 hours since I am studying. The time right now is 12:45. He is coming today. I study till midnight everyday. It takes 2 mins to solve this problem. He is coming in January. He went abroad on 2nd March, 1999. He was working here 5 years ago.
Output(with temporal expression enclosed within square bracket:
I get up in the [morning] at [6 am]
I have been playing cricket since [2004]
My birth date is [1997/9/8]
It has been [2 hours] since I am studying
The time right [now] is [12:45]
He is coming [today]
I study till [midnight] [everyday]
It takes [2 mins] to solve this problem
He is coming in [January]
He went abroad on [2nd March], [1999]
He was working here 5 years [ago]